Development of nomogram prediction model for postoperative recurrence of HCC patients undergoing liver transplantation in Chinese population with internal validation
Ensi Ma1, Jianhua Li1, Zhengxin Wang1.
1General surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
Background: Recurrence prediction models for hepatocellular carcinoma liver transplantation in western countries already exist, but the differences in tumor biological characteristics among different populations. So we aim to create a Nomogram prediction model for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma liver transplantation patients in China to predict individual survival after surgery and guide the postoperative treatment.
Materials and Methods: Between February 2016 and October 2019, 210 HCC patients who received liver transplantation in the Huashan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University were collected for this study. Prognostic nomograms predicting post-transplant recurrence were developed from a multivariate cox regression. The prediction power of the nomograms was tested by C-statistic and calibration plots.
Results: There were 46(21.9%) patients within the Milan criteria. Before transplantation,24(11.4%) patients received transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) and 9(4.3%) received tumor targeted therapy.Multivariate predictors of recurrence included Age,Max diameter,thrombus,MVI,ALT on the 7th day after surgery(7d-ALT),AFP on the 7th day after surgery(7d-AFP). Nomogram for recurrence free survival (RFS) have been created. Discrimination and calibration of the nomograms revealed good predictive abilities(C-index:0.796).
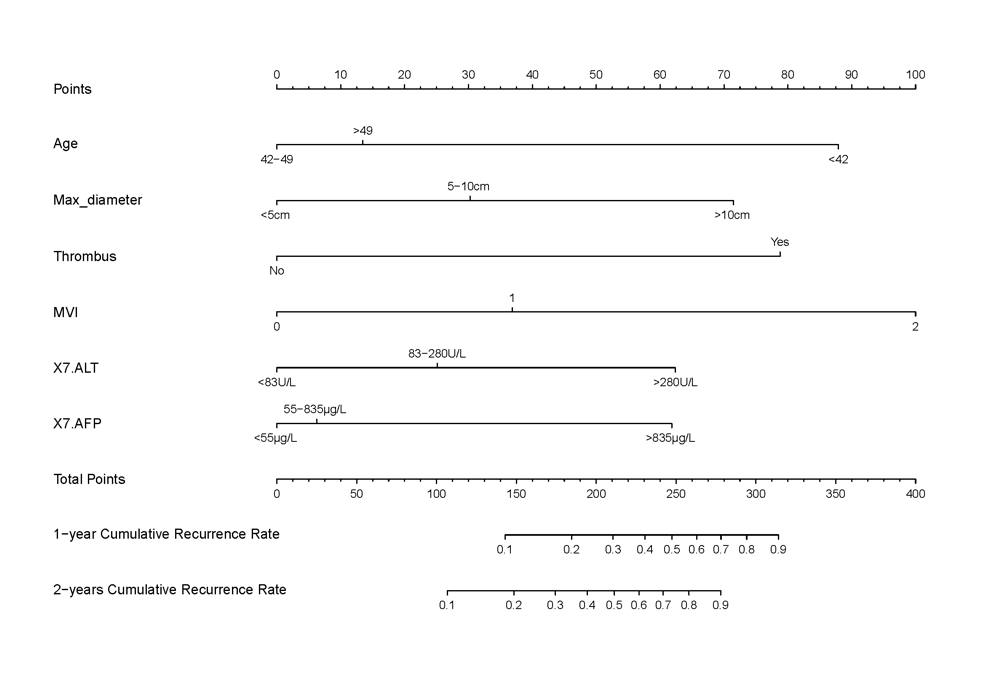
Compared with Milan criteria(C-index:0.617), UCSF criteria(C-index:0.624), the RFS nomogram improved accuracy in predicting recurrence after transplantation for HCC.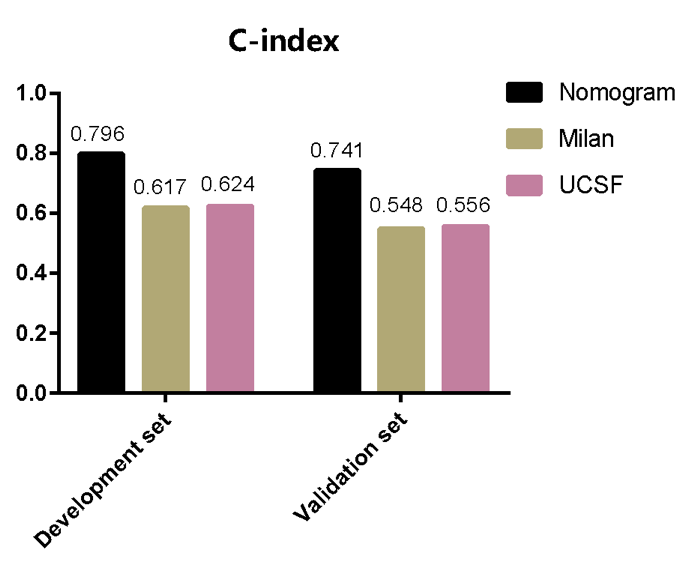
Finally, two subgroups were generated based on the total risk points . The 1,2,3-year recurrence rate were 16.6%,23.3%,26.9%for the low risk group,and 52.4%,80.1%,80.1% for the high risk group, respectively.
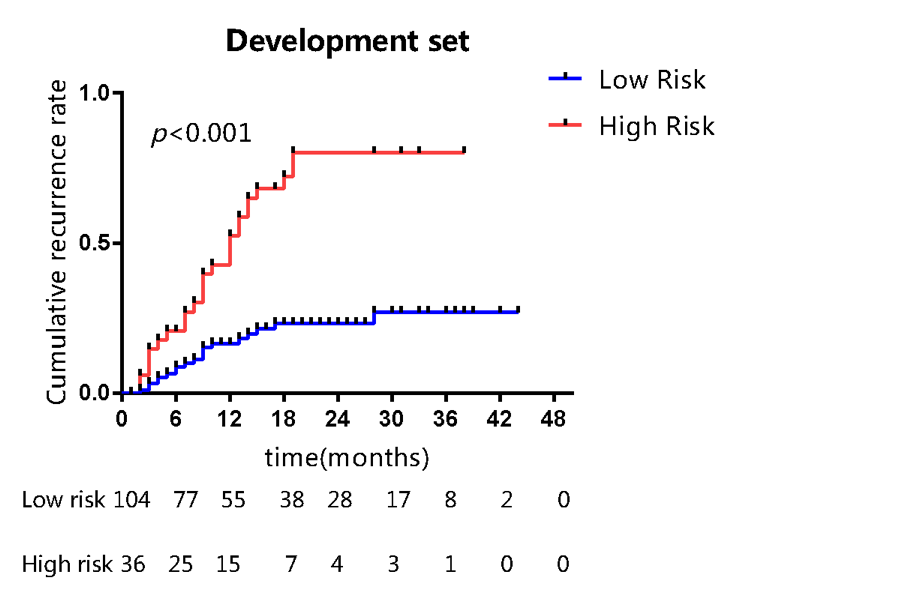
Conclusion: The nomogram made by using different examination indexes had good ability in predicting prognostic recurrence and guiding the follow-up of patients.It can achieve patient stratification and guide patients for treatment and follow-up.Patients with score above 312.1 points had high risk of early recurrenceafter LT.For these patients, more strict postoperative targeted treatment and follow-up are needed.
In order to be convenient and practical, we have also made web prediction models for convenience and practicality.For example, a 45 year old male (0 point), tumor maximum diameter of 7cm (30.3 points), have tumor thrombus (78.8 point), MVI of 1 (36.9 points), ALT of 156u / L (25.1 points), AFP of 83 μ g / L (6.2 points) on the 7th day after operation. For this example, the total score is 177.3 points, so the predicted recurrence rate of 1 and 2 years is 18% and 31%. This calculated value can be used to develop treatment plans and communicate with patients.
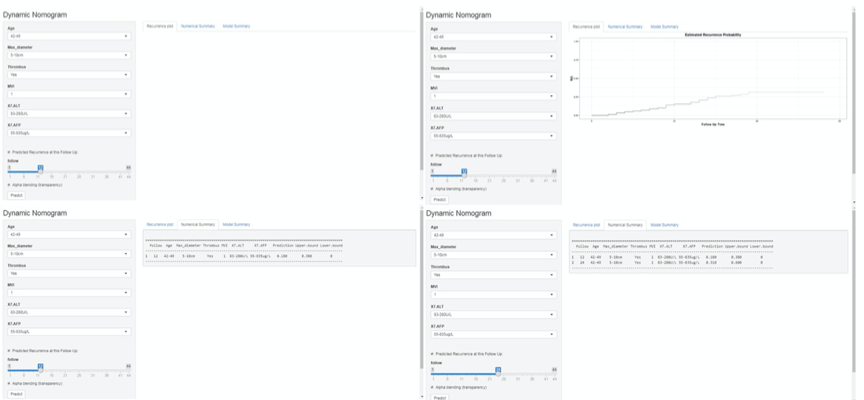
https://maensi.shinyapps.io/Huashan_surgery/
There are no comments yet...