Risk of hematological malignancies in solid organ transplant recipients: a meta-analysis
Runchen Wang1, Zhenyu Huo1, Fan Ge2, Yaokai Wen1, Hengrui Liang4, Yu Jiang1, Zixuan Su1, Weiyi Lin2, Wenhua Liang3, Jianxing He4.
1Nanshan School, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China; 2The First Clinical College, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China; 3Department of Thoracic oncology, The 1st Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China; 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, The 1st Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China
Introduction: Patients underwent solid organ transplantation are considered to be associated with an increased risk of developing hematological malignancies. We performed a meta-analysis to determine whether there was an increased risk of hematological malignancies in solid organ transplant recipients.
Materials and Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, Medline were searched. Random-effects model meta-analyses were used to calculate standardized incidence ratios (SIRs) for solid organ transplant recipients versus the general population, stratified by types of hematological malignancies (leukemia, lymphoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and multiple myeloma). Subgroup analyses were performed based on transplant type of each study.
Results and Discussion: Based on data from 565,153 patients in 52 studies, in solid organ transplant recipients, we identified a 6-fold higher risk of hematological malignancies (SIR: 6,24 [95%Cl: 2.48 - 7.16, p<0.001]). Among them, a 2.47-fold risk of leukemia (SIR: 2.47 [95% CI :1.74 - 3.50, p<0.001]), a 3.01-fold risk of multiple myeloma (SIR: 3.01 [95% CI: 2.29 – 3.95, P<0.001]), a 9.13-fold SIR of lymphoma (SIR: 9.13 [95% CI: 7,12 – 11.70, P<0.001], a 11.41-fold risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (SIR: 11.41 [95%Cl: 9.74 - 13.36, p<0.001]), and a 4.50-fold risk of Hodgkin's lymphoma (SIR: 4.50 [95% CI: 3.33 – 6.08, P<0.001]), compared with the general population. In subgroup analyses, we found that heart and/or lung transplant recipients has the highest SIRs compared with kidney or liver transplant recipients (Table 1).
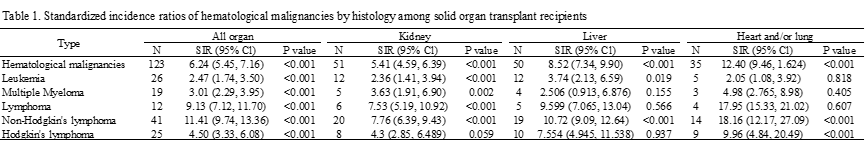
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that solid transplant recipients showed a significantly greater risk of hematological malignancies, which varied among different transplantation types. Such association can provide guidance for clinicians in the detection of hematological malignancies among solid organ transplantation recipients.
[1] Adami J, Gäbel H, Lindelöf B, Ekström K, Rydh B, Glimelius B, et al. Cancer risk following organ transplantation: a nationwide cohort study in Sweden. British journal of cancer. 2003;89(7):1221-7.
[2] Collett D, Mumford L, Banner NR, Neuberger J, Watson C. Comparison of the incidence of malignancy in recipients of different types of organ: a UK Registry audit. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2010;10(8):1889-96.
[3] Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM, Fraumeni JF, Jr., Kasiske BL, Israni AK, Snyder JJ, et al. Spectrum of cancer risk among US solid organ transplant recipients. JAMA. 2011;306(17):1891-901.
[4] Hortlund M, Arroyo Mühr LS, Storm H, Engholm G, Dillner J, Bzhalava D. Cancer risks after solid organ transplantation and after long-term dialysis. International journal of cancer. 2017;140(5):1091-101.
[5] Na R, Grulich AE, Meagher NS, McCaughan GW, Keogh AM, Vajdic CM. Comparison of de novo cancer incidence in Australian liver, heart and lung transplant recipients. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2013;13(1):174-83.
[6] O'Neill JP, Sexton DJ, O'Leary E, O'Kelly P, Murray S, Deady S, et al. Post-transplant malignancy in solid organ transplant recipients in Ireland, The Irish Transplant Cancer Group. Clinical transplantation. 2019;33(10):e13669-e.
[7] Park B, Yoon J, Choi D, Kim HJ, Jung YK, Kwon OJ, et al. De novo cancer incidence after kidney and liver transplantation: Results from a nationwide population based data. Scientific reports. 2019;9(1):17202-.
[8] Serraino D, Piselli P, Busnach G, Burra P, Citterio F, Arbustini E, et al. Risk of cancer following immunosuppression in organ transplant recipients and in HIV-positive individuals in southern Europe. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England : 1990). 2007;43(14):2117-23.
[9] Tsai H-I, Lee C-W, Kuo C-F, See L-C, Liu F-C, Chiou M-J, et al. De novo malignancy in organ transplant recipients in Taiwan: a nationwide cohort population study. Oncotarget. 2017;8(22):36685-95.
[10] Wareham NE, Li Q, Sengeløv H, Da Cunha-Bang C, Gustafsson F, Heilmann C, et al. "Risk of de novo or secondary cancer after solid organ or allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation". Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology. 2019;145(12):3125-35.
[11] Agraharkar ML, Cinclair RD, Kuo Y-F, Daller JA, Shahinian VB. Risk of malignancy with long-term immunosuppression in renal transplant recipients. Kidney international. 2004;66(1):383-9.
[12] Agraharkar ML, Cinclair RD, Kuo Y-F, Daller JA, Shahinian VB. Risk of malignancy with long-term immunosuppression in renal transplant recipients. Kidney international. 2004;66(1):383-9.
[13] Birkeland SA, Løkkegaard H, Storm HH. Cancer risk in patients on dialysis and after renal transplantation. Lancet (London, England). 2000;355(9218):1886-7.
[14] Buxeda A, Redondo-Pachón D, Pérez-Sáez MJ, Bartolomé Á, Mir M, Pascual-Dapena A, et al. Gender differences in cancer risk after kidney transplantation. Oncotarget. 2019;10(33):3114-28.
[15] Cheung CY, Lam MF, Chu KH, Chow KM, Tsang KY, Yuen SK, et al. Malignancies after kidney transplantation: Hong Kong renal registry. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2012;12(11):3039-46.
[16] Heo J, Noh OK, Oh Y-T, Chun M, Kim L. Cancer risk after renal transplantation in South Korea: a nationwide population-based study. BMC nephrology. 2018;19(1):311-.
[17] Hoshida Y, Tsukuma H, Yasunaga Y, Xu N, Fujita MQ, Satoh T, et al. Cancer risk after renal transplantation in Japan. International journal of cancer. 1997;71(4):517-20.
[18] Kessler M, Jay N, Molle R, Guillemin F. Excess risk of cancer in renal transplant patients. Transplant international : official journal of the European Society for Organ Transplantation. 2006;19(11):908-14.
[19] Kim JH, Kim S-O, Han DJ, Park S-K. Post-transplant malignancy: a burdensome complication in renal allograft recipients in Korea. Clinical transplantation. 2014;28(4):434-42.
[20] Kyllönen L, Salmela K, Pukkala E. Cancer incidence in a kidney-transplanted population. Transplant international : official journal of the European Society for Organ Transplantation. 2000;13 Suppl 1:S394-S8.
[21] Li W-H, Chen Y-J, Tseng W-C, Lin M-W, Chen T-J, Chu S-Y, et al. Malignancies after renal transplantation in Taiwan: a nationwide population-based study. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association. 2012;27(2):833-9.
[22] Mazzucotelli V, Piselli P, Verdirosi D, Cimaglia C, Cancarini G, Serraino D, et al. De novo cancer in patients on dialysis and after renal transplantation: north-western Italy, 1997-2012. Journal of nephrology. 2017;30(6):851-7.
[23] Opelz G, Unterrainer C, Süsal C, Döhler B. Immunosuppression with mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor and incidence of post-transplant cancer in kidney transplant recipients. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association. 2016;31(8):1360-7.
[24] Piselli P, Serraino D, Segoloni GP, Sandrini S, Piredda GB, Scolari MP, et al. Risk of de novo cancers after transplantation: results from a cohort of 7217 kidney transplant recipients, Italy 1997-2009. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England : 1990). 2013;49(2):336-44.
[25] Ramsey-Goldman R, Brar A, Richardson C, Salifu MO, Clarke A, Bernatsky S, et al. Standardised incidence ratios (SIRs) for cancer after renal transplant in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and non-SLE recipients. Lupus science & medicine. 2016;3(1):e000156-e.
[26] Schrem H, Schneider V, Kurok M, Goldis A, Dreier M, Kaltenborn A, et al. Independent Pre-Transplant Recipient Cancer Risk Factors after Kidney Transplantation and the Utility of G-Chart Analysis for Clinical Process Control. PloS one. 2016;11(7):e0158732-e.
[27] Teo SH, Lee K-G, Lim GH, Koo SX, Ramirez ME, Chow KY, et al. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of malignancies after kidney transplantation in Singapore: a 12-year experience. Singapore medical journal. 2019;60(5):253-9.
[28] Tessari G, Naldi L, Boschiero L, Minetti E, Sandrini S, Nacchia F, et al. Incidence of primary and second cancers in renal transplant recipients: a multicenter cohort study. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2013;13(1):214-21.
[29] Vajdic CM, McDonald SP, McCredie MRE, van Leeuwen MT, Stewart JH, Law M, et al. Cancer incidence before and after kidney transplantation. JAMA. 2006;296(23):2823-31.
[30] Villeneuve PJ, Schaubel DE, Fenton SS, Shepherd FA, Jiang Y, Mao Y. Cancer incidence among Canadian kidney transplant recipients. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2007;7(4):941-8.
[31] Aberg F, Pukkala E, Höckerstedt K, Sankila R, Isoniemi H. Risk of malignant neoplasms after liver transplantation: a population-based study. Liver transplantation : official publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society. 2008;14(10):1428-36.
[32] Baccarani U, Piselli P, Serraino D, Adani GL, Lorenzin D, Gambato M, et al. Comparison of de novo tumours after liver transplantation with incidence rates from Italian cancer registries. Digestive and liver disease : official journal of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver. 2010;42(1):55-60.
[33] Chatrath H, Berman K, Vuppalanchi R, Slaven J, Kwo P, Tector AJ, et al. De novo malignancy post-liver transplantation: a single center, population controlled study. Clinical transplantation. 2013;27(4):582-90.
[34] Ettorre GM, Piselli P, Galatioto L, Rendina M, Nudo F, Sforza D, et al. De novo malignancies following liver transplantation: results from a multicentric study in central and southern Italy, 1990-2008. Transplantation proceedings. 2013;45(7):2729-32.
[35] Heo J, Noh OK, Oh Y-T, Chun M, Kim L. Second primary cancer after liver transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide population-based study. Hepatology international. 2017;11(6):523-8.
[36] Hsiao C-Y, Lee P-H, Ho C-M, Wu Y-M, Ho M-C, Hu R-H. Post-transplant malignancy in liver transplantation: a single center experience. Medicine. 2014;93(28):e310-e.
[37] Jiang Y, Villeneuve PJ, Fenton SSA, Schaubel DE, Lilly L, Mao Y. Liver transplantation and subsequent risk of cancer: findings from a Canadian cohort study. Liver transplantation : official publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society. 2008;14(11):1588-97.
[38] Jiang Y, Villeneuve PJ, Fenton SSA, Schaubel DE, Lilly L, Mao Y. Liver transplantation and subsequent risk of cancer: findings from a Canadian cohort study. Liver transplantation : official publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society. 2008;14(11):1588-97.
[39] Kaneko J, Sugawara Y, Tamura S, Aoki T, Sakamoto Y, Hasegawa K, et al. De novo malignancies after adult-to-adult living-donor liver transplantation with a malignancy surveillance program: comparison with a Japanese population-based study. Transplantation. 2013;95(9):1142-7.
[40] Maggi U, Consonni D, Manini MA, Gatti S, Cuccaro F, Donato F, et al. Early and late de novo tumors after liver transplantation in adults: the late onset of bladder tumors in men. PloS one. 2013;8(6):e65238-e.
[41] Nordin A, Åberg F, Pukkala E, Pedersen CR, Storm HH, Rasmussen A, et al. Decreasing incidence of cancer after liver transplantation-A Nordic population-based study over 3 decades. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2018;18(4):952-63.
[42] Oo YH, Gunson BK, Lancashire RJ, Cheng KK, Neuberger JM. Incidence of cancers following orthotopic liver transplantation in a single center: comparison with national cancer incidence rates for England and Wales. Transplantation. 2005;80(6):759-64.
[43] Schrem H, Kurok M, Kaltenborn A, Vogel A, Walter U, Zachau L, et al. Incidence and long-term risk of de novo malignancies after liver transplantation with implications for prevention and detection. Liver transplantation : official publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society. 2013;19(11):1252-61.
[44] Sérée O, Altieri M, Guillaume E, De Mil R, Lobbedez T, Robinson P, et al. Longterm Risk of Solid Organ De Novo Malignancies After Liver Transplantation: A French National Study on 11,226 Patients. Liver transplantation : official publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society. 2018;24(10):1425-36.
[45] Sheiner PA, Magliocca JF, Bodian CA, Kim-Schluger L, Altaca G, Guarrera JV, et al. Long-term medical complications in patients surviving > or = 5 years after liver transplant. Transplantation. 2000;69(5):781-9.
[46] Taborelli M, Piselli P, Ettorre GM, Lauro A, Galatioto L, Baccarani U, et al. Risk of virus and non-virus related malignancies following immunosuppression in a cohort of liver transplant recipients. Italy, 1985-2014. International journal of cancer. 2018;143(7):1588-94.
[47] Jäämaa-Holmberg S, Salmela B, Lemström K, Pukkala E, Lommi J. Cancer incidence and mortality after heart transplantation - A population-based national cohort study. Acta oncologica (Stockholm, Sweden). 2019;58(6):859-63.
[48] Jiang Y, Villeneuve PJ, Wielgosz A, Schaubel DE, Fenton SSA, Mao Y. The incidence of cancer in a population-based cohort of Canadian heart transplant recipients. American journal of transplantation : official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons. 2010;10(3):637-45.
[49] Kellerman L, Neugut A, Burke B, Mancini D. Comparison of the incidence of de novo solid malignancies after heart transplantation to that in the general population. The American journal of cardiology. 2009;103(4):562-6.
[50] Krynitz B, Edgren G, Lindelöf B, Baecklund E, Brattström C, Wilczek H, et al. Risk of skin cancer and other malignancies in kidney, liver, heart and lung transplant recipients 1970 to 2008--a Swedish population-based study. International journal of cancer. 2013;132(6):1429-38.
[51] Ekstrom M, Riise GC, Tanash HA. Risk of cancer after lung transplantation for COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:2841-7.
[52] Fink AK, Yanik EL, Marshall BC, Wilschanski M, Lynch CF, Austin AA, et al. Cancer risk among lung transplant recipients with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2017;16(1):91-7.
[53] Magruder JT, Crawford TC, Grimm JC, Kim B, Shah AS, Bush EL, et al. Risk Factors for De Novo Malignancy Following Lung Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(1):227-38.
[54] Ohman J, Rexius H, Mjornstedt L, Gonzalez H, Holmberg E, Dellgren G, et al. Oral and lip cancer in solid organ transplant patients--a cohort study from a Swedish Transplant Centre. Oral Oncol. 2015;51(2):146-50.
There are no comments yet...
