Establishment of early diagnostic model of acute rejection in combination with IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α and IFN-γ
Zhankui Jin1,2, CuiXiang Xu1,2, Puxun Tian2.
1Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Third Affiliated Hospital of Medical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, People's Republic of China; 2Kidney Transplantation, First Affiliated Hospital of Medical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, People's Republic of China
Introduction: As kidney transplant recipients need to take immunosuppressants for a long time after operation, the expression level of immune molecules in peripheral blood is low, which often leads to low sensitivity and specificity to predict acute rejection and delay diagnosis. We combined in vitro lymphocyte stimulation with flow cytometry to detect four indicators of IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α and IFN-γ to establish a non-invasive diagnosis model of acute rejection. And evaluate its ability to early warning and non-invasive diagnosis of acute rejection. Further explore a simple and effective method for predicting rejection in clinical practice.
Methods: Fifty two kidney transplant recipients underwent kidney transplantation with living-related donor were selected as objects and divided into two groups that stable allograft function (STA, n=30) and acute rejection (AR, n=22). Stimulate all objects peripheral venous blood for 8 hours by phorbol myfismte acetate and ionomycin, and detect the expression of cell culture supernatant IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α and IFN-γ by flow cytometry.The study was approved by the local ethical committee. IL-2 greater than 34.88 is defined as positive, less than 34.88 is defined as negative; IL-6 greater than 143.26 is defined as positive, and less than 143.26 is defined as negative; TNF-α greater than 98.25 is defined as positive, and less than 98.25 is defined as negative; IFN-γ is greater than 88.36 Defined as positive, less than 88.36 is defined as negative.
Results: We will combine in vitro lymphocyte stimulation with flow cytometry to detect four indicators of IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α and IFN-γ to establish a non-invasive diagnosis model of acute rejection. We established four non-invasive diagnostic models for acute rejection (Table 1), and found that Model 3, which is a model with three or more positive diagnostic indicators, has the strongest ability to diagnose acute rejection with the largest Youden index (0.80).
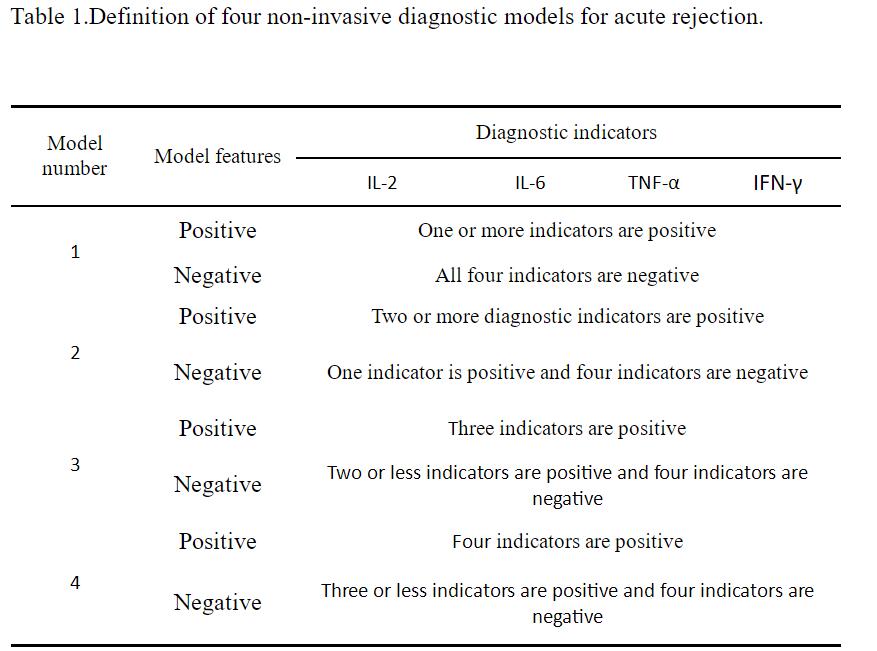
The specificity was 86.36% and 93.33%, and the positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 90.48% and 90.32%, respectively (Table 2).
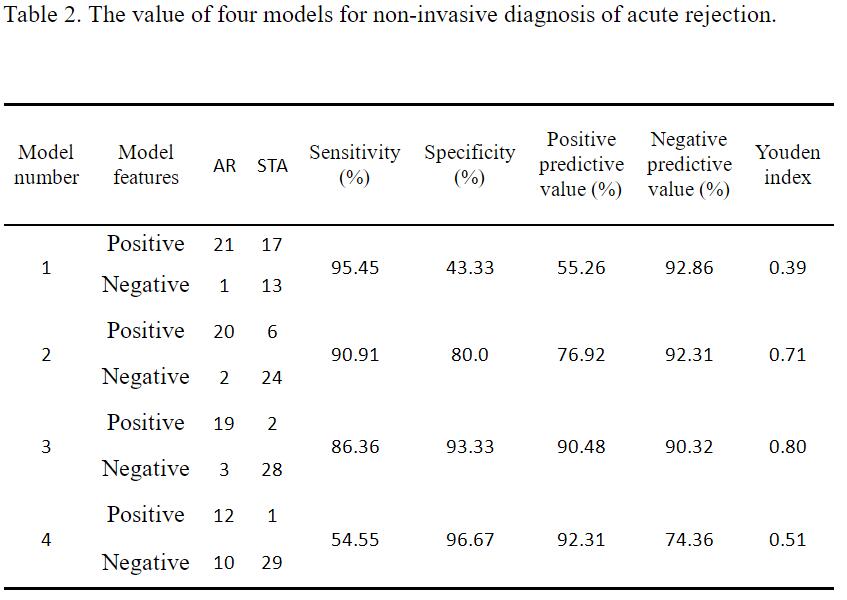
Model 3 has a better ability for noninvasive diagnosis of acute rejection than the other three models, becoming the best noninvasive diagnostic model for acute rejection in this study.
Conclusions: We combined the in vitro lymphocyte stimulation with flow cytometry to detect four indicators of IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α and IFN-γ, and established four non-invasive diagnostic models of acute rejection. Among these four models, the sensitivity and specificity of non-invasive diagnosis of acute rejection in models with three or more positive indicators were 86.36% and 93.33%.
There are no comments yet...
