A prediction model of delay graft function from deceased donor risk factor: A multi-center study from China
Wujun Xue1, Yang Li1, Jin Zheng1, Xiaojun Hu1, Chenguang Ding1, Changxi Wang2, Xuyong Sun3, Jianghua Chen4, Xiaotong Wu5, Longkai Peng6, Zhishui Chen7, Qingshan Qu8, Xiaodong Zhang9, Yaowen Fu10, Zhen Dong11, Zheng Chen12.
1Department of renal transplantation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, People's Republic of China; 2Department of renal transplantation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China; 3Department of renal transplantation, People's Liberation Army 923 Hospital, Nanning, People's Republic of China; 4Center of nephrology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, People's Republic of China; 5Department of renal transplantation, the Second Hospital of Shanxi People, Taiyuan, People's Republic of China; 6Department of renal transplantation, the Second Xiangya Hosptial of Central South University, Changsha, People's Republic of China; 7Department of renal transplantation, Tongji Hospital of Huazhong Scientific and Technology University, Wuhan, People's Republic of China; 8Department of renal transplantation, the Hospital of Zhengzhou People, Zhengzhou, People's Republic of China; 9Department of urinary surgery, Chaoyang Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing, People's Republic of China; 10Department of urinary surgery, the First Affiliated Baiqiuen Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, People's Republic of China; 11Department of renal transplantation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, People's Republic of China; 12Department of renal transplantation, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China
Background: The quality of deceased donation seriously increased the incidence of delayed graft function (DGF) after renal transplantation. However, there is still no recognized donor evaluation system for DGF prediction in China. This study investigated the impact of donor risk factor on DGF and developed a donor risk score system for DGF prediction.
Methods: A total of 1807 deceased donors and 3599 their donated renal transplant performed in 22 center of China were included this retrospective study. Associations of DGF with the clinical characteristics of donors were quantified by univariate analysis. A donor risk scoring system was developed by multivariate logistic regression and validated using an independent sample.
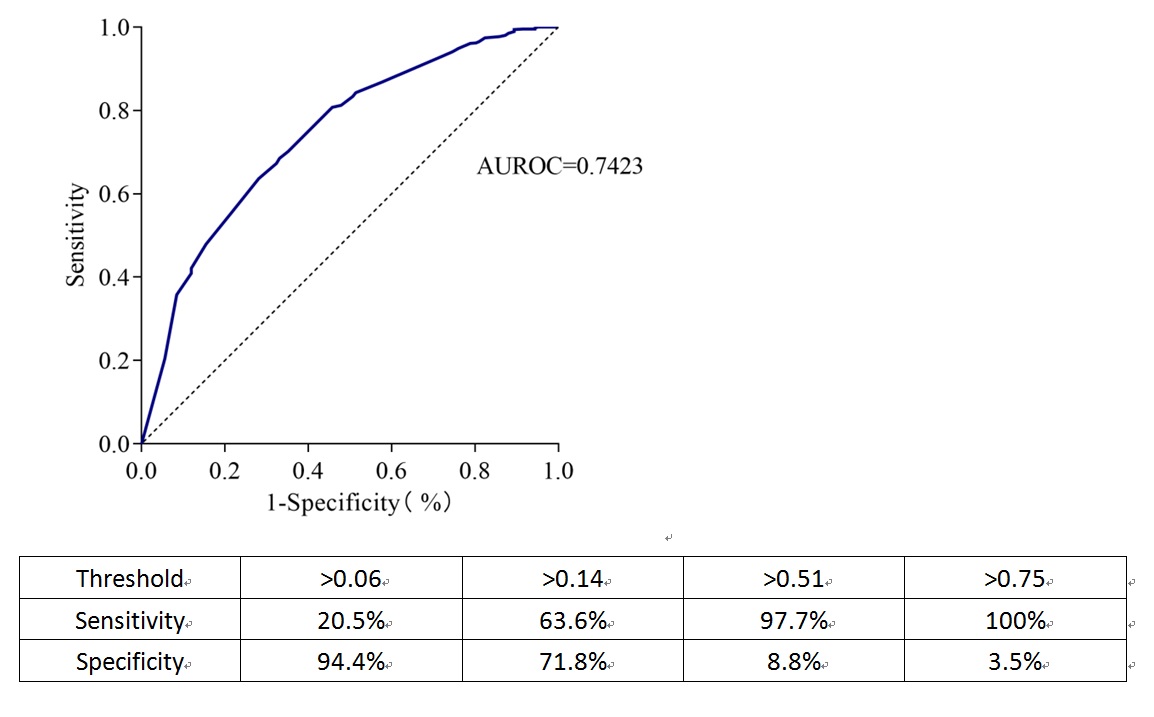
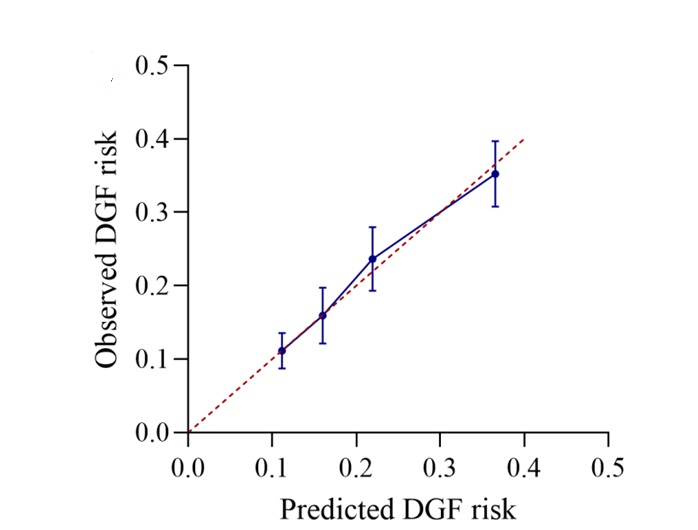
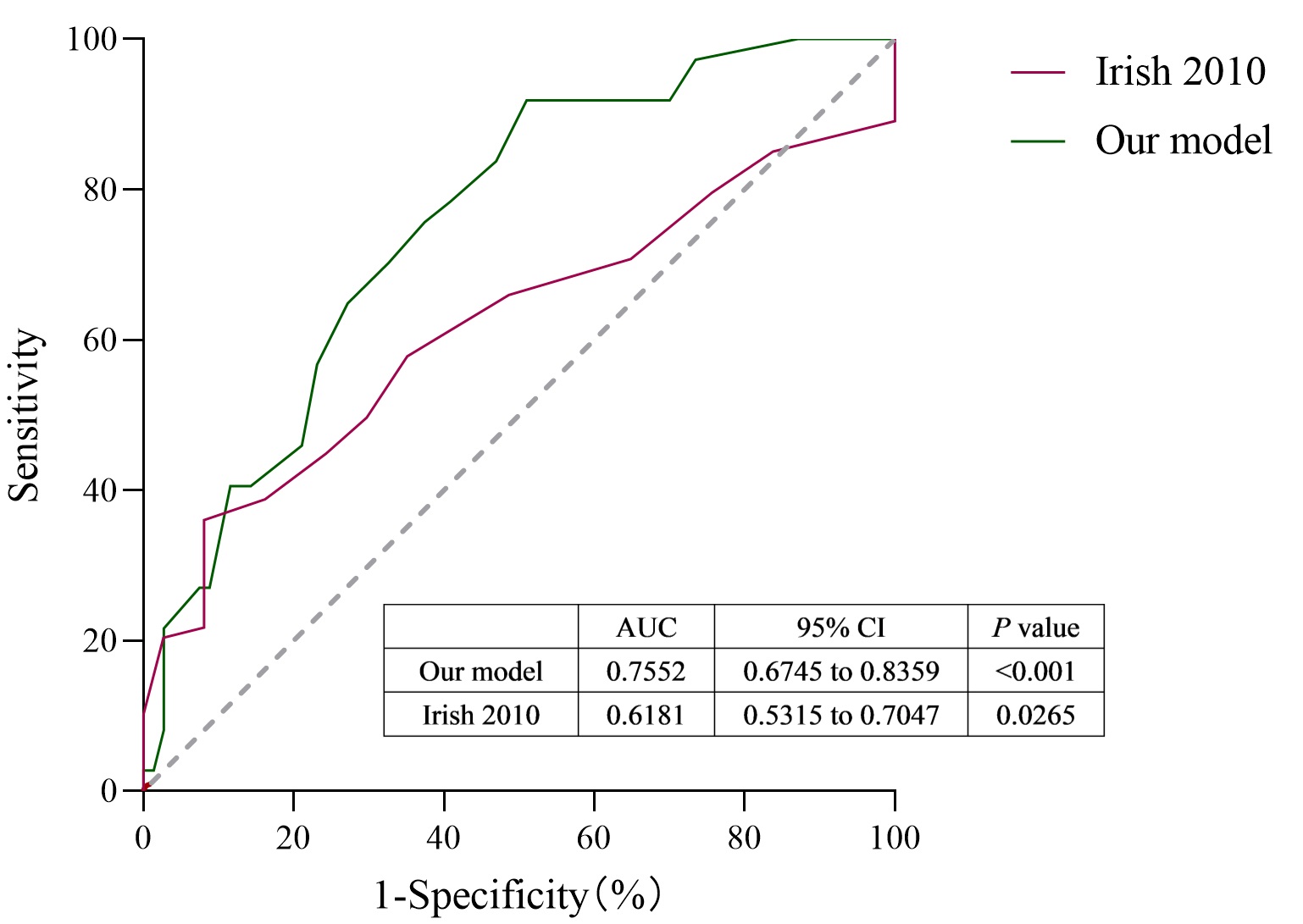
Results: In this retrospective multi-center study, the incidence of DGF was 18.7% from donor aspect. Six donor characteristics and different layings including age, primary disease, hypertension history, terminal serum creatininer, and hypotension persistent and CPR tine were risk factors of DGF. A 49-point score system of donor risk was established for DGF prediction which showed a good degree of discrimination. The prediction model was achieved an area under the curve of 0.7423 (95% CI 0.69-0.79) in predicting DGF in internal validation. The AUROC was 0.7552 (95% CI0.67-0.84) in external validation by a independent one center sample compared to Irish model which demonstrated an AUROC of 0.6181 (95% CI 0.53-0.70).
Conclusion: The study determined deceased donor risk factors related to DGF after renal transplantation in China and firstly develop a scoring system in line with the characteristics of the Chinese population for DGF prediction more effectively. The scoring system had good diagnostic significance and consistency and can be used by clinicians to make evidence-based decisions on the use of renal from deceased donor and guiding renal transplantation therapy.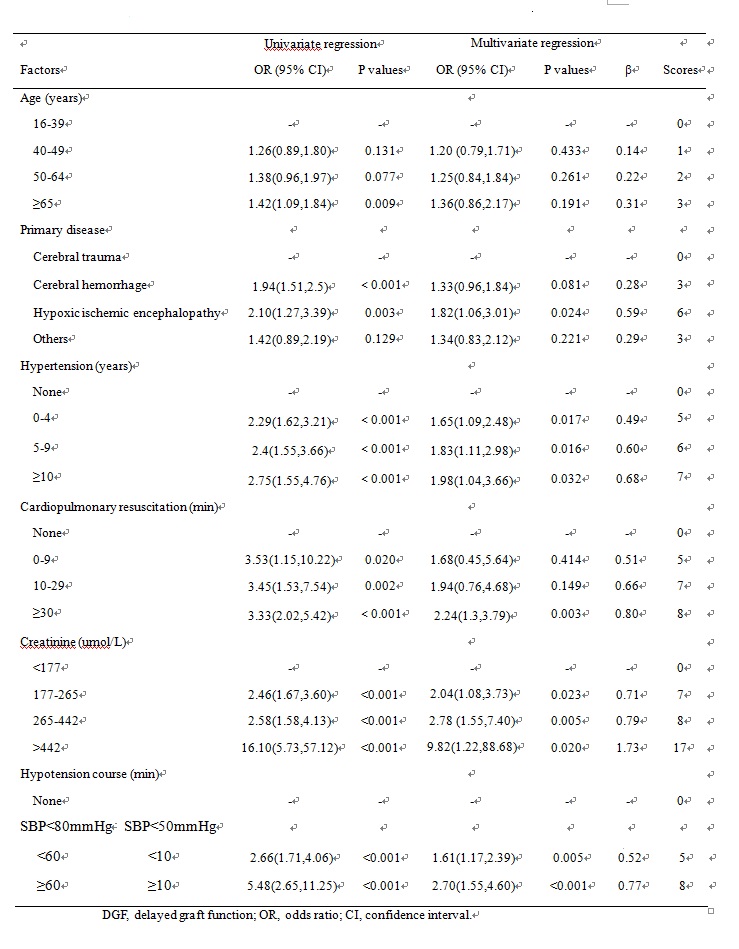
[1] Mallon DH. DGF after renal transplantation. Transplantation. 2013;96:885-889.
[2] Siedlecki A. Delayed graft function in the kidney transplant. AM J Transplant. 2011; 11:2279-2296.
[3] Xue W. Outcomes for kidney transplantation from DD in China. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17:250.
There are no comments yet...
