
Impact of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in post renal transplant: A single center experience
Rutul M. Dave1, Nilav M. Shah2, Dinesh N. Gera1, Vivek B. Kute1, Divyesh P. Engineer1, Himanshu V. Patel1, Shubho Banerjee1.
1Nephrology and Transplantation Medicine, IKDRC-ITS HOSPITAL, Ahmedabad, India; 2Nephrology and Transplantation Medicine, Bhavnagar Institute of Medical science, Bhavnagar, India
Objectives: To study incidence, risk factors, manifestations, effect of prophylaxis with antiviral, graft and patient survival in post renal transplant recipients with CMV.
Introduction: CMV is a virus of HHV5 family. It is a common organism involved in infectious complications after transplantation. The disease can be caused by transmission from the transplanted organ, due to reactivation of latent infection, or after a primary infection in sero-negative transplant patients. The incidence is 8-32% post-transplant. The risk factors for CMV infection are organ from a seropositive donor in sero-negative recipient (D+/R-), increased net IS, other co morbid conditions (Diabetes, Hepatitis C virus etc.).
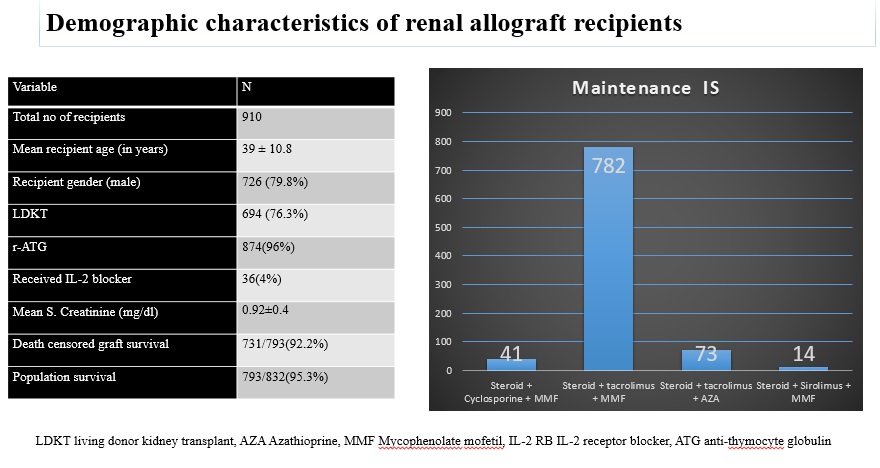
Materials and Methods: Retrospective analysis of 910 post renal transplant recipients with mean follow-up of 1±0.6 years. The serostatus of patients and donors determined by ELISA & CMV infection by CMV DNA detection with a PCR. r-ATG and IL-2RB were used as induction agents. Maintenance IS was given with steroid, CNI and an antimetabolite agent. Acute cellular rejections treated with r-ATG. Acute antibody mediated rejections treated with PLEX with IVIG and Rituximab. Valganciclovir prophylaxis given to patients 3 months post-transplant and injection of r-ATG/Rituximab. Oral valgancyclovir or IV ganciclovir for 3- 4 weeks with weekly monitoring of CMV DNA. Co-trimoxazole prophylaxis was advised lifelong. Dosage modified according to eGFR and side effects.
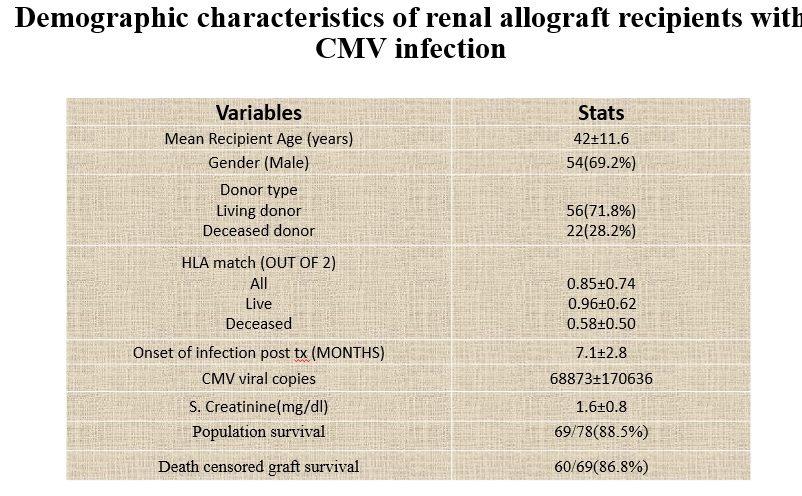
Results and Discussion: 78(8.6%) out of 910, patients were diagnosed with CMV. The mean age was 42 ± 11.6 years, with 69.2% (54/78) being male. Malaise (61.53%) and Fever (51.28%) were the commonest presenting symptoms. Diabetes (21.8%) and hepatitis C virus (14.1%) the commonest comorbid conditions. CMV disease was seen in 8.7% & 5.6% of patients with r-ATG & IL-2RB as induction therapy, respectively. 16/78(20.5%) patients had rejection episode. 65.4% patients developed CMV after 6 months post-transplantation. Over mean follow-up of 1 ± 0.8 years, patient and graft survival rates were 85.9% and 70.5%, respectively with mean serum creatinine level was 1.6 ± 0.76 mg/dl.
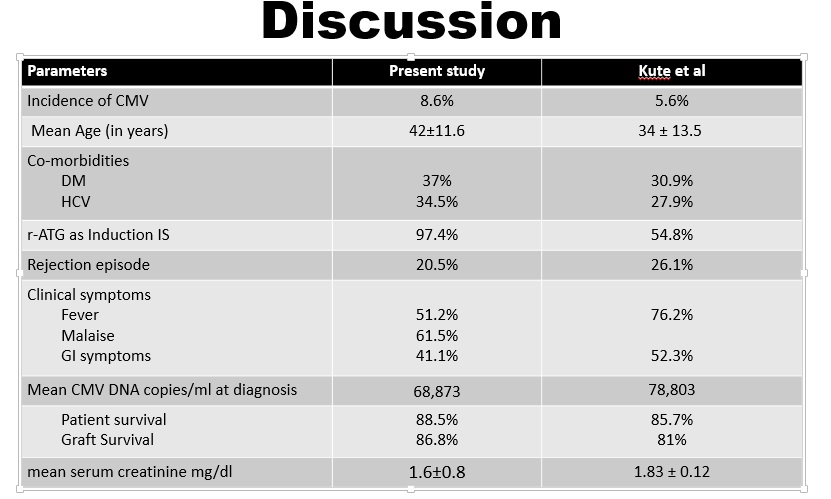
These outcomes were comparable to previous study conducted by Kute et al at our center in 2009-’12.
Conclusion: We found low incidence of CMV infection as well as milder form of disease due to universal prophylaxis of valganciclovir and also due to low dosage of r-ATG (1-2mg/kg) as induction therapy. The use of antivirals would prevent both viral replication and disease.
Keywords: Cytomegalovirus – CMV, post-renal transplant patient, ATG- Anti-thymocyte globulin, living donor kidney transplant- LDKT, Azathioprine- AZA, Mycophenolate mofetil- MMF, IL-2 receptor blocker- IL-2 RB, IS- immunosuppression, anti-thymocyte globulin- ATG, Plasma exchange- PLEX, Calcinurin inhibitor- CNI, estimated Glomerular filteration rate- eGFR
[1] Murray BM, Brentjens J, Amsterdam D, Myers J, Gray V, Pawlowski I, Schewegler K, Singh JP (1997) Monitoring and diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 8(9):1448–1457
[2] Murray BM, Subramaniam S (2004) Late cytomegalovirus infection after oral ganciclovir prophylaxis in renal transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis 6(1):3–9
[3] Mourad G, Rostaing L, Legendre C, Garrigue V, Thervet E, Duran D (2004) Sequential protocols using basiliximab versus antithymocyte globulins in renal-transplant patients receiving mycophenolate mofetil and steroids. Transplantation 78(4):584–590
[4] Pour-Reza-Gholi F, Labibi A, Farrokhi F, Nafar M, Firouzan A, Einollahi B (2005) Signs and symptoms of cytomegalovirus disease in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 37:3056–3058
[5] Farrugia E, Schwab TR (1992) Management and prevention of cytomegalovirus infection after renal transplantation. Mayo Clin Proc 67:879
[6] V.B. Kute, A.V. Vanikar, P.R. Shah et al: Post–Renal Transplant Cytomegalovirus Infection: Study of Risk Factors; Transplantation Proceedings, 44, 706–709 , 2012
There are no comments yet...
