Teriparatide in kidney transplant patients with severe hypocalcemia
Luis Leon1, Maria Rial1, Ana Uriona1, Olga Guardia1, Domingo Casadei1.
1Renal Transplant, d.INSTITUTE-ITAC-Nephrology, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Introduction: severe hypocalcaemia after surgical parathyroidectomy, in kidney transplanted patients, leads to the intake of high doses of calcium, magnesium and calcitriol in addition to poor quality of life. PTH1-34 (teriparatide) is a therapeutic option in these cases.
Methods: A series of 10 renal transplanted patients with post-parathyroidectomy symptomatic hypocalcaemia due to tertiary hyperparathyroidism treated with subcutaneous teriparatide due to inadequate response to high doses of calcium and calcitriol are reported.
Synthetic PTH (Teriparatide) was indicated in doses of 20ug / day and the behavior of calcium levels (VN 3.8-5 mg / dl), phosphatemia (VN 2.3-4.7mg / dl), magnesemia (VN 1.3-2.1mequ / lt), renal function were evaluated (creat VN 0.6-1.10mg / dl) as well as requirements for calcium, magnesium and calcitriol and adverse events associated with the treatment.
Results: 10 patients, 6 males, 9BD, 1 LD. Average age 45.32 ± 11.75 years, etiology 5 unknown, 2 GMP, 1 UHS, 1 APKD and 1 obstructive uropathy. 8 parathyroidectomized patients-two pre-transplant and 2 at 4 years post-transplant.
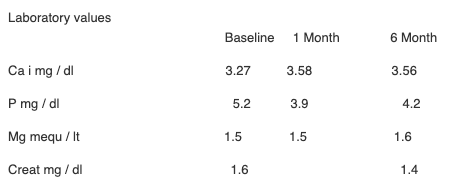
An increase in Cai values (baseline 3.27 vs 1 month 3.58 (p 0.05), Baseline vs 6 month 3.56 (p 0.03)) could be observed without statistical value in P, Mg and Creat values. The dose of calcium and magnesium was decreased by 20% and calcitriol was discontinued after one month after starting treatment.
1 patient discontinued treatment due to episodes of symptomatic hypotension one month after initiation.
The dose of 20 ug was maintained in all patients except in 2 that required 40ug / day
Conclusion: in this group of patients, an adequate response to teriparatide treatment was observed, correcting the calcemia without altering renal function.
There are no comments yet...
