Survival analysis in the presence of competing risks in kidney transplant
Sergio Salcedo1, Andrea Garcia1, Nasly Patiño1, Jefferson Barbosa1, Sergio Riveros1, Juan Garcia1, Jessica Pinto Ramirez1, Fernando Giron1.
1Kidney Transplantation , Colombiana de Trasplantes, Bogota, Colombia
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a multisystemic pathology with great clinical impact on the quality of life of patients and their families; and commits approximately 10% of the world's population.
In patients with stage 4 and 5, kidney transplantation is the therapy choice; it has shown improvement towards quality of life, survival and decrease in costs.
The survival of a functional graft has been described around 88% at 5 years and 72-87% at 10 years; however, new statistical models for analyzing survival data have recently been developed.
Objective: Describe the survival of the renal graft between the conventional survival analysis and the competitive risk analysis
Methods: A retrospective analytical study of a historical cohort in Colombiana de Trasplantes, Bogota Colombia, was carried out, including transplant patients between 2008-2019.
Results: 1520 subjects included, 619 receiving patients were women (40.7%). The average age of the patients was 43.58 +/- 13.23 years. Absolute risk of graft loss by conventional survival analysis was 73% at ten years and competing-risk analysis .was 75% at ten years. The risk calculated by conventional methods reflects a hypothetical scenario in which graft loss and all other events are censored. The risk calculated by competing-risk analysis reflects the probability of a graft loss in a real-world scenario, whereby death from other causes is taken into account.
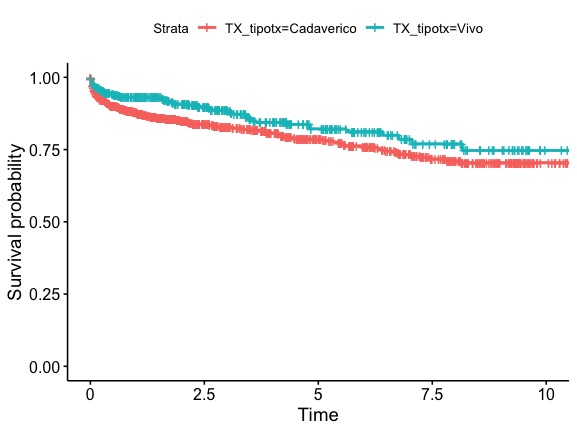
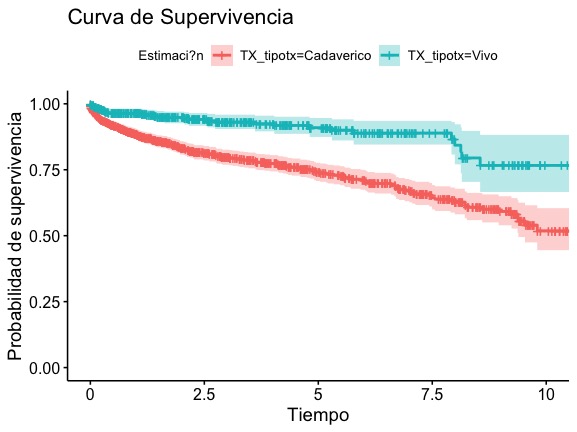
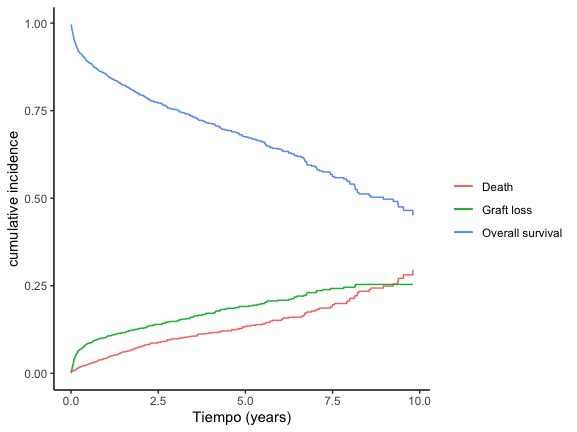
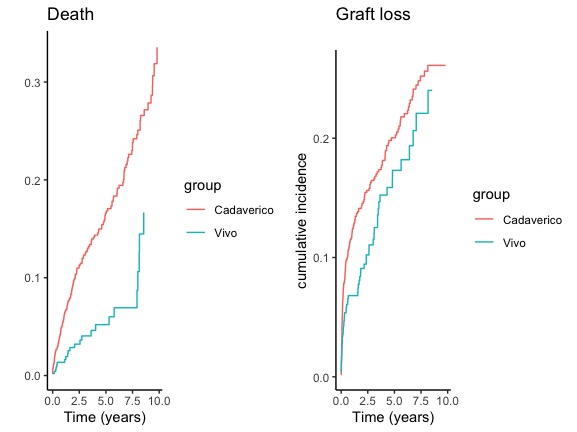
Conclusions: When estimating probability of long term graft survival and death, competing risk analysis gives more accurate measure in subgroups with different rate of competing event.
Keywords: Kidney trasplantation, graft survival, registry-based studies, retrospective studies.
[1] Costo CDEA. LA ENFERMEDAD RENAL CRÓNICA, LA HIPERTENSIÓN ARTERIAL Y LA DIABETES MELLITUS en Colombia. 2017; Available from: https://cuentadealtocosto.org/site/images/Publicaciones/Situacion_ERC_HA_DM_Colombia_2016.pdf
[2] Martínez-Mier G, Ávila-Pardo SF, Irigoyen-Castillo A, Rodríguez-Fernández A, Jiménez-López LA, Varela-Pérez V. Análisis de la supervivencia a 10 años de trasplante renal en el Hospital de Alta Especialidad de Veracruz. Artículo Orig [Internet]. 2016;5:113–9. Available from: http://www.medigraphic.com/trasplantes%0Awww.medigraphic.org.mx
[3] Dávila FA, Pareja MJ, Rodríguez ES, Fajardo WR, Luna RD, Flórez K V. Análisis de supervivencia del trasplante renal (cohorte retrospectiva). Urol Colomb. 2017;26(1):12–6.
[4] Rodríguez Vidal M, Parra Morales M, Rocha Ortiz S, Castro Salas M, Villalobos Sepúlveda C. Supervivencia del injerto y del receptor en el trasplante renal en el hospital Guillermo Gran Benavente (Concepción, Chile). Enfermería Nefrológica [Internet]. 2014;17(4):292–8.
[5] Angeles L, Dis- K. M O R TA L I T Y I N PAT I E N T S O N D I A LYS I S A N D T R A N S P L A N T R EC I P I E N T S COMPARISON OF MORTALITY IN ALL PATIENTS ON DIALYSIS , PATIENTS ON DIALYSIS AWAITING TRANSPLANTATION , AND RECIPIENTS OF A FIRST. 1999;1725–30.

Jessica Pinto Ramirez
2020-09-12 16:18
Thanks