
ATG- F (Grafalon) vs Thymoglobulin( r ATG ) as an induction agent in living donor renal transplant: A retrospective single centre experience
Abhyudaysingh Rana1, Shyam bihari Bansal 1, Pranaw Jha1, Amit kumar Mahapatra1, Ashish Nandwani1, Manish Jain1, Dinesh Yadav 1, Dinesh Bansal 1, Sidharth Sethi1, Ashwini Gadde1, Vijay Kher1.
1Department of Nephrology and Renal transplant , Medanta - The Medicity , Gurugram, India
Introduction: The best modality of renal replacement therapy for patients with end stage renal disease is kidney transplantation. Induction agents play a crucial role in preventing acute rejection which also has bearing on long term graft outcomes. Lymphocyte depleting induction agents commonly used include r ATG (Thymoglobulin), ATG-F (Grafalon) & Alemtuzumab. In this study we compare Grafalon (ATG-F) with r ATG(Thymoglobulin) as induction agent for living donor renal transplant.
Materials and Methods: This was a single centre retrospective study. All the patients who underwent living donor renal transplant at our centre since January 2017 with minimal follow up of 3 months were included. Retransplants & deceased donor transplants were excluded. ATG-F (Grafalon) was given at 6 mg /kg (2 divided doses) & r ATG (Thymoglobulin ) at 3 mg/kg (2 divided doses) doses followed by triple immunosupression (Tacrolimus +MMF +Steroids) . Acute graft dysfunction was defined as a 25% increase in serum creatinine level from baseline. All acute rejection episodes were biopsy proven.
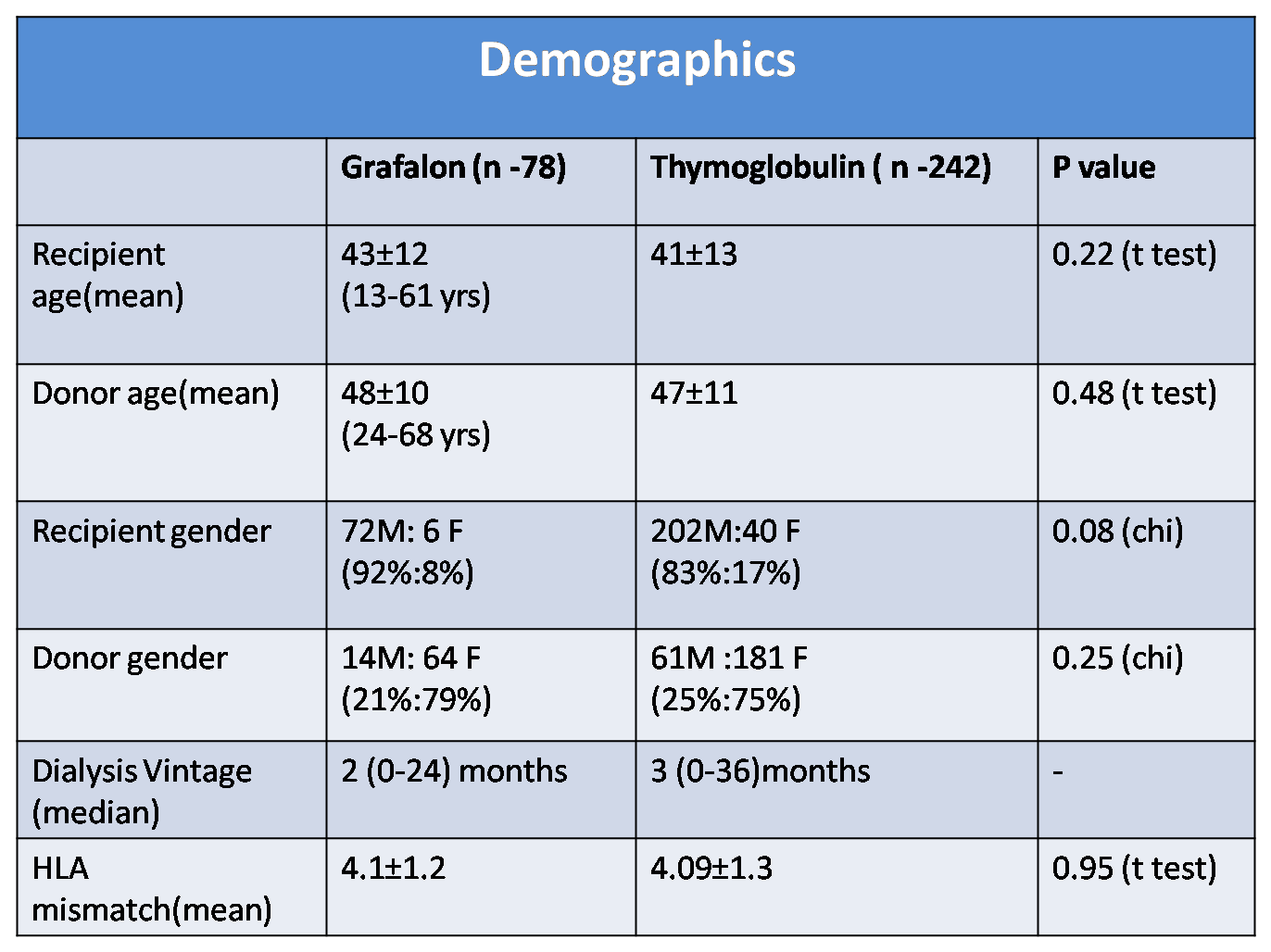
Results: During the study period 570 living donor renal transplants were done. Patients were followed up for median duration of 22 months (3-35 months). r ATG(Thymoglobulin) was given to 242 (42.4%) patients whereas 78 (13.6%) patients received ATG-F(Grafalon) as induction agent.
Mean recipient age was 43±12 years in ATG-F group vs 41±13 yrs in r ATG group (p=0.22) & mean donor age was 48±10 years(ATG-F) vs 47±11 yrs(r ATG) (p=0.48) . Recipients were predominantly male (92 % ,83% p =0.08) while donors were predominantly female (79% ,75% p=0.25) in both the groups.
Mean HLA mismatch was 4.1±1.2(ATG-F) vs 4.09±1.3(r ATG) p=0.95. The proportion of ABO and HLA incompatible transplants were comparable in both the groups. Incidence of BPAR was 11.5% vs 4.5 % in ATG-F vs Thymoglobulin group( p = 0.03)
Incidence of infection was comparable in both the groups (12.8% vs 14.46%, p=0.86). Two patients in Graflon group had BKV nephropathy while 2 patients in rATG had CMV infection. Mean serum creatinine level at follow up of 22 months (Median) was 1.26±0.35 mg/dl (ATG F ) & 1.18±0.34 mg/dl (r ATG) (p =0.07) .
Patient survival(p =1) & graft survival (p=0.24) were comparable in both the groups. One patient lost graft due to drug non compliance in grafalon group while there was no death censored graft loss in thymoglobulin group. There was no incidence of PTLD in either group and the incidence of NODAT was similar in both groups (5.1% vs 5.7% ,p =1)
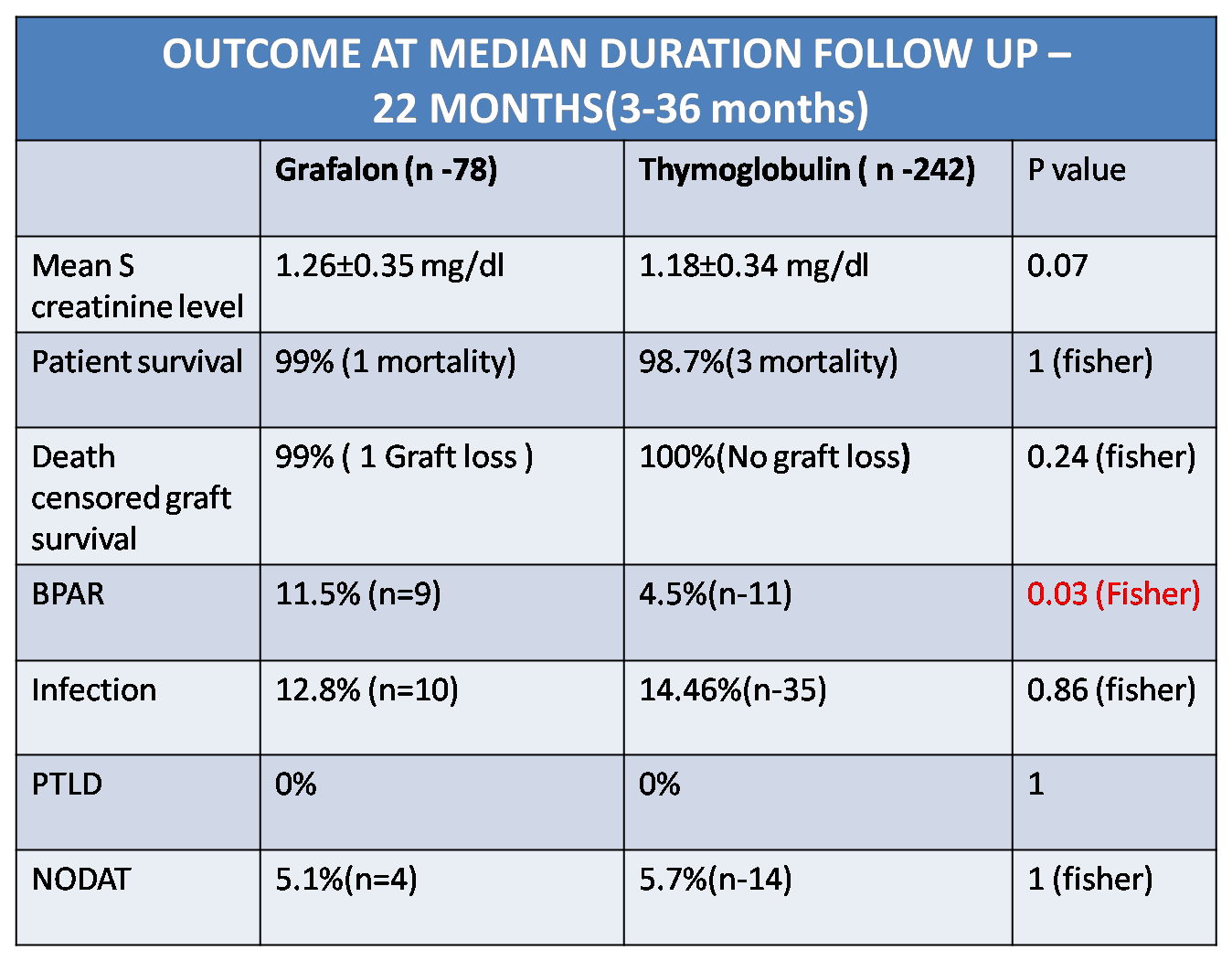
Conclusion: ATG-F (Grafalon- 6mg/kg dose) use as an induction agent was associated with significantly higher rate of biopsy proven acute rejection as compared to r ATG (Thymoglobulin-3mg/kg dose) with comparable short term graft survival, patient survival and infection rate.
There are no comments yet...